A rare but alarming condition, colloquially referred to as the “bleeding eye disease,” has recently captured public attention due to its distressing symptoms and potential health risks. Though not widespread, this disease demands awareness and timely medical intervention to mitigate complications. Here’s everything you need to know about its symptoms, available treatments, and the role of vaccination in prevention.
Understanding the Disease
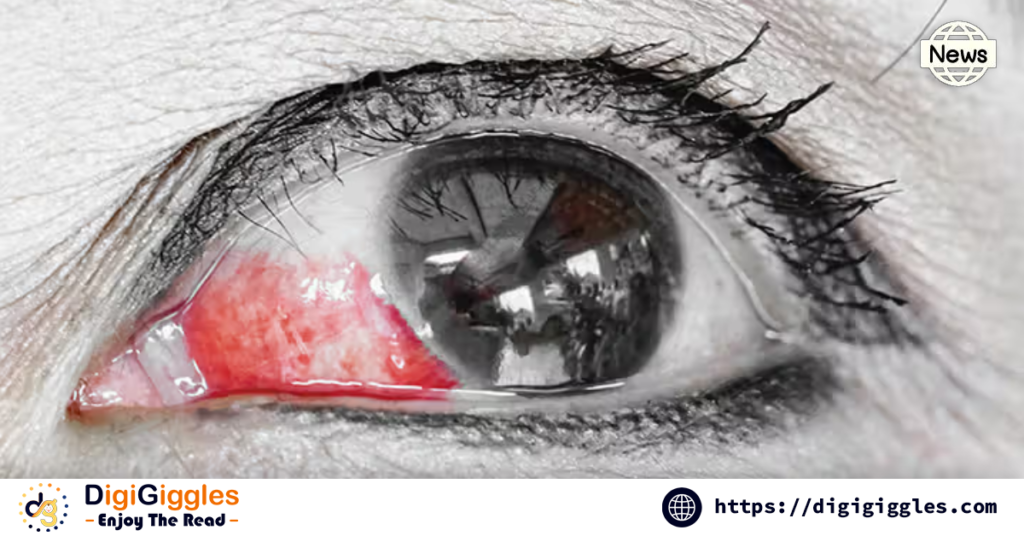
The term “bleeding eye disease” is not an official medical designation but rather a descriptor for severe eye infections or inflammations characterized by subconjunctival hemorrhage—bleeding beneath the surface of the eye. It can result from viral or bacterial infections, injuries, or underlying health conditions like hypertension. Experts highlight that while the sight of blood in the eye may appear alarming, not all cases are critical. However, some infections associated with this condition, such as adenovirus conjunctivitis, may spread rapidly, particularly in close-contact settings like schools or workplaces.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Key symptoms to watch out for include:
- Red or Bloodshot Eyes: Caused by bleeding under the conjunctiva.
- Pain and Swelling: Often accompanying redness, making it difficult to open the eyes.
- Blurred Vision: Temporary visual disturbances are common.
- Discharge and Itching: Signs of an infection.
- Fever and Fatigue: Indicating a systemic viral infection.
If you notice these symptoms persisting or worsening, consult an ophthalmologist immediately. Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent complications like corneal ulcers or vision loss.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Viral infections often resolve on their own within a week or two, with supportive care such as lubricating eye drops and cold compresses. For bacterial infections, antibiotic eye drops or ointments are prescribed. In severe cases involving underlying conditions, systemic medications or surgical interventions may be required. Preventive measures include maintaining good hygiene, avoiding the sharing of personal items like towels, and refraining from touching your eyes with unclean hands.
The Role of Vaccination
A preventive vaccine for bleeding eye disease does not currently exist as it is often caused by various unrelated factors. However, vaccinations against diseases like measles, rubella, and adenovirus indirectly reduce the risk of some conditions leading to eye complications. Medical researchers are exploring targeted vaccines as awareness about the condition grows.
Stay Vigilant and Informed
The “bleeding eye disease” serves as a stark reminder of the importance of eye health. While not every case signifies a serious problem, timely medical consultation ensures peace of mind and proper care. As one expert aptly said, “Your eyes are your window to the world—never take them for granted.” Stay informed, prioritize hygiene, and consult professionals at the earliest sign of trouble to safeguard your vision.